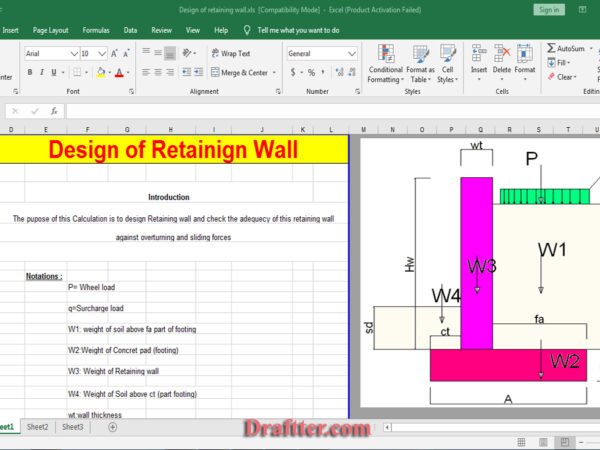
Description
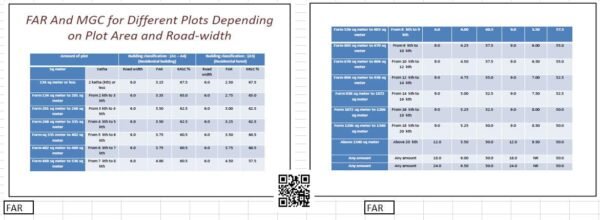
FAR and MGC
Floor Area Ratio (FAR) and Maximum Ground Coverage (MGC) are critical metrics in the realm of urban planning and architectural design. They serve as essential tools for determining the permissible building size and the footprint that structures can occupy on a specific parcel of land. Understanding these concepts is fundamental for architects, city planners, and developers, as they aim to create functional and aesthetically pleasing environments while adhering to regulatory frameworks.
The Floor Area Ratio is defined as the ratio of a building’s total floor area to the total area of the land upon which it is built. This metric essentially dictates how much floor space can be constructed on a given site, facilitating efficient land usage. By regulating FAR, urban planners can manage building density and promote sustainable development practices, ensuring that urban landscapes do not become overcrowded or unbalanced. FAR is particularly crucial in densely populated areas, where space is at a premium and the architectural designs must maximize usable area while maintaining livability.
On the other hand, Maximum Ground Coverage refers to the percentage of the lot that can be covered by the building’s footprint. It complements FAR by providing a complementary guideline that focuses on the ground-level space that structures occupy. MGC helps in maintaining open spaces within urban environments, thus enhancing the quality of life for residents and balancing natural and built elements. Both FAR and MGC are vital for compliance with local zoning regulations, giving municipal authorities control over urban development patterns.
These calculations are frequently utilized by various stakeholders including architects who design buildings within regulatory constraints and city planners who work to create balanced neighborhoods. By understanding FAR and MGC, all parties can ensure that their projects meet local laws while fulfilling community needs and aspirations.
Using the RAJUK Sheet for FAR and MGC Calculations
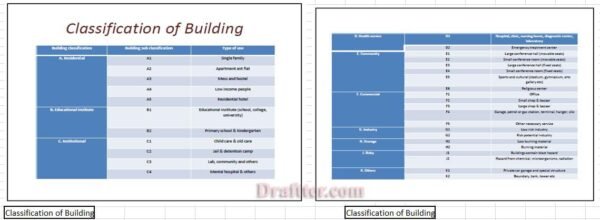
The RAJUK (Rajdhani Unnayan Kartripakkha) sheet serves as an essential tool for architects, urban planners, and developers in calculating Floor Area Ratio (FAR) and Maximum Ground Coverage (MGC) for various construction projects. This particular sheet is structured to provide a clear and organized format, ensuring participants can efficiently input data and derive the necessary calculations. Within the RAJUK sheet, users will encounter several critical fields, including plot area, built-up area, and permissible FAR and MGC values. Proper understanding of these components is vital for accurate calculations.
To effectively use the RAJUK sheet, begin by inputting the total plot area in the designated field. Next, you will need to fill in the intended built-up area of the project. The FAR is then calculated by dividing the built-up area by the plot area. It is crucial to ensure that the calculated FAR does not exceed the permissible limits set by local regulations, thus ensuring compliance.
Additionally, the MGC calculation can also be achieved through the RAJUK sheet by providing the ground floor area and comparing it against the total plot area. The formula for MGC follows a similar principle, necessitating careful attention to square footage to avoid exceeding the limits. It is frequently observed that common errors arise from miscalculating these areas or misinterpreting the local regulations regarding permissible ratios.
When interpreting the results generated by the RAJUK sheet, it is recommended to cross-reference them against local building codes and guidelines to confirm that the proposed design meets all legal requirements. This cross-referencing will also help identify any discrepancies early in the planning process, thereby preventing costly adjustments later. By following these outlined steps diligently, stakeholders can ensure their submissions are well-calibrated and align with the necessary regulatory frameworks.









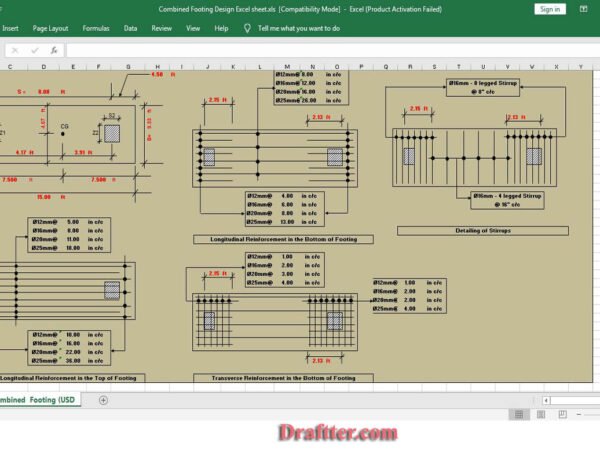


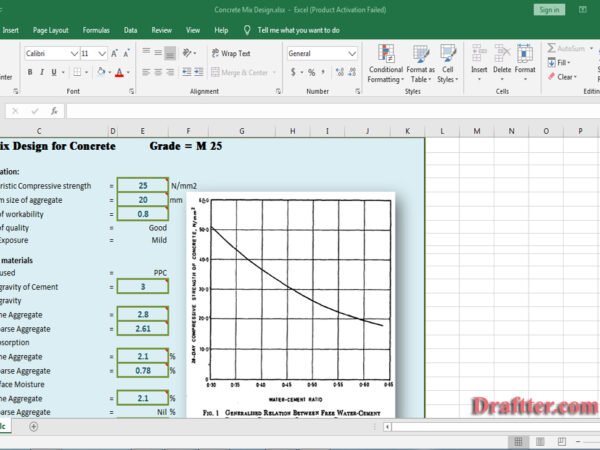
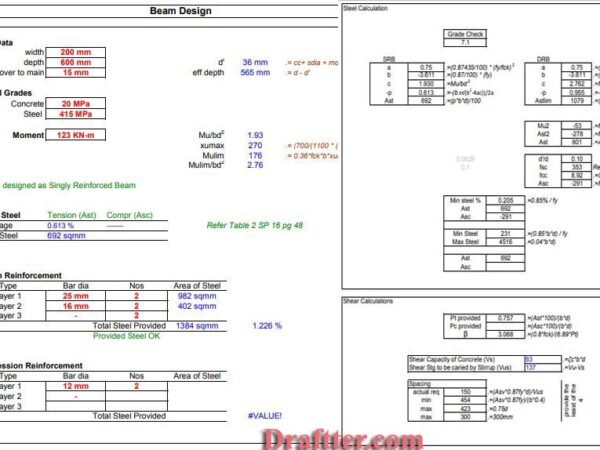
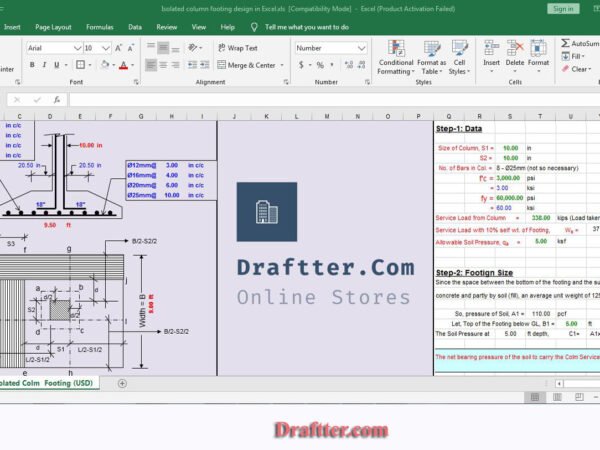
Architect Rokonuzzaman –
Draftter’s “Understanding Floor Area Ratio (FAR) and Maximum Ground Coverage (MGC) Calculators with RAJUK Sheets” is an essential Excel sheet for architects, urban planners, and developers. The step-by-step guide provides the know-how to calculate permissible building areas and footprints, ensuring efficient land use, sustainable development, and compliance with local zoning regulations. Its clarity and organization facilitate smooth calculations and contribute to functional and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. Absolutely indispensable for responsible, well-informed urban planning and architectural design.